Validation Controls in ASP.NET
Validation controls are very useful while submitting data into a database table. These controls prevent users from submitting the wrong type of data.
By default, the validation controls perform validation on both the client (the browser) and the server. These validation controls uses JavaScript to perform validation on client-side. Client side validation is very fast because user gets immediate response whenever user enters an invalid value into a form field. Sometimes browsers (mobile browsers) do not support javascript. If a browser does not support JavaScript, then server side validation still perform.
There are six validation controls available in the ASP.NET.
- RequiredFieldValidator
- RangeValidator
- CompareValidator
- RegularExpressionValidator
- CustomValidator
- ValidationSummary
1. RequiredFieldValidator Control
The RequiredFieldValidator control ensures that the input field is not empty.
The Syntax of the control is given:

Important Properties:
| Properties |
Description |
| ControlToValidate |
The ID of the control for which Required FieldValidator control will be associated. |
| Error Message |
This property is used to show the error message, if the user forgets to enter the data, then custom error message will appear. |
You have to set the above two given property in all the ASP.NET validation control. These two properties are common to all validation control except ValidationSummary control.
2. RangeValidator Control
RangeValidator confirms that user input data is within a specified range of values.
The input value should come between a certain minimum and maximum value otherwise it will give error.
The Syntax of the control is given:

Important Properties:
| Properties |
Description |
| MinimumValue |
The minimum value of the validation range. |
| MaximumValue |
The maximum value of the validation range. |
| Type |
It defines the type of the data. Possible values are String, Integer, Date and Currency. |
3. CompareValidator
CompareValidator control is used to compare the value of one form field against another field or with a fixed value.
The Syntax of the control is given:
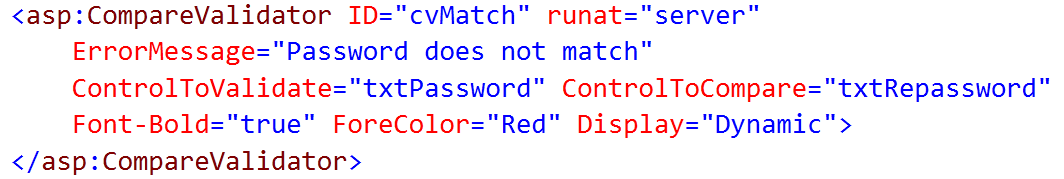
Important Properties:
| Properties |
Description |
| ControlToCompare |
The ID of a control against which to compare. |
| ValueToCompare |
The fixed value against which to compare. |
| Type |
The type of value for comparison like String, Integer, Double, Date and Currency. |
| Operator |
It specifies the comparison operator like Equal, NotEqual, GreaterThan, GreaterThanEqual, LessThan, LessThanEqual, and DataTypeCheck. |
4. RegularExpressionValidator
The RegularExpressionValidator allows validating the input text by matching against a pattern of a regular expression.
The regular expression is set in the ValidationExpression property.
The Syntax of the control is as given:

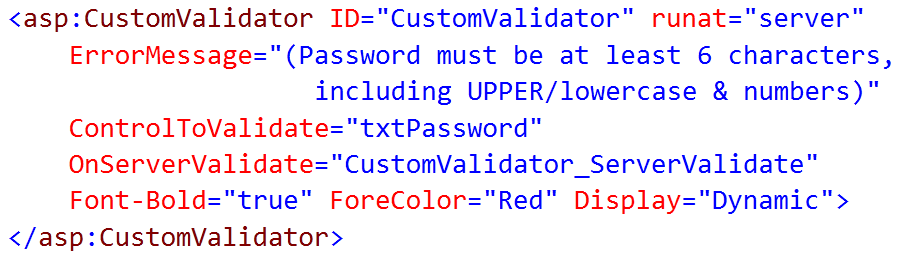
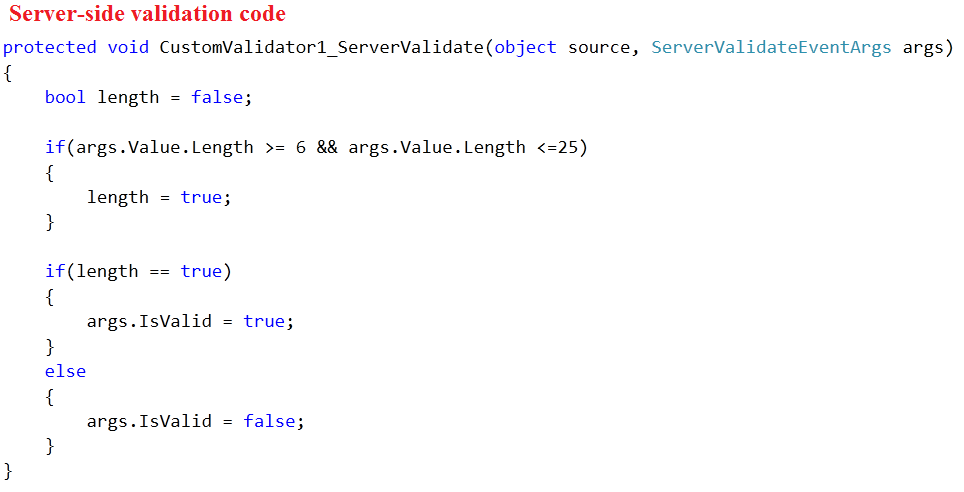
5. CustomValidator
CustomValidator control enables you to create your own validation. The CustomValidator control performs validation, based upon the code, you write. We can write validation code that will be executed on the client side or with server-side validation.
The Syntax for the control is as given:
6. ValidationSummary
The ValidationSummary control does not perform any validation but shows a summary of all errors in the page.
This control summarizes the error messages for all validation controls on a Web page in a single location. ValidationSummary control is useful when working with large forms.
If a user enters the wrong value in the field located at the end of the page, then the user might never see the error message. ValidationSummary control can displays a list of errors at the top of the form. It does not support ErrorMessage and ControlToValidate property. It automatically displays the error message in the form of MessageBox or summary.
By default ShowMessageBox property value is set False and ShowSummary property value is set True. You can use these properties according to your need.
Important Properties:
| Properties |
Description |
| DisplayMode: |
BulletList, List and SingleParagraph |
| HeaderText: |
Display header text above the validation summary. |
| ShowMessageBox: |
It is used to display a popup alert box. |
| ShowSummary: |
It shows the error messages in specified format. |
Menu vs Tab
| Menu |
Tabs |
| Menu are used to segregate data which might not be inter-related. |
Tabs are used to segregate data which are somehow related. |
| By clicking on the menu, will redirect to different page. |
By clicking on tab, will redirect to the current page but differnt content. |
| Some menu items may have sub-menu items that are displayed in a drop down menu. |
Tabs usually do not contain drop down like menu. |
 |
Application file types used in ASP.NET
The following list provides a good representation of the file types that you may encounter during ASP.NET development.
| File Name |
Description |
| .aspx |
A web form that may include a code-behind file. |
| Web.config |
Configuration file which hold setting for application |
| Global.asax |
File is used to declare global variables and react to global events. |
| .html |
A standard HTML page. |
| .css |
A Cascading Style Sheet that may be used within the site. |
| .js |
Javascript Page |
| .asax |
This file allows you to write code to handle global ASP.NET application-level events. The file has a name of global.asax, which you cannot change. |
| .ashx |
A page for implementing a generic handler. |
| .sitemap |
A web application's site map. |
| .browser |
A browser definition file. |
| .ascx |
A web user contorl |
How can web page be made interactive?
| SOCIAL MEDIA: |
Adding a Facebook like button or the option to share a post from your site in Facebook or Twitter is a way to add basic interaction with your users. |
| FEEDBACK AND RATINGS: |
Asking for feedback is a good idea to see what users think and feel about your site or featured products. |
| FREQUENT UPDATES: |
Users are more likely to return to a frequently updated site since they view it as a more reliable source of information. |
Master Page in ASP.NET
A master page in ASP.NET provides a template for other pages, with shared layout and functionality. The master page defines placeholders for the content, which can be overridden by content pages. The output result is a combination of the master page and the content page.
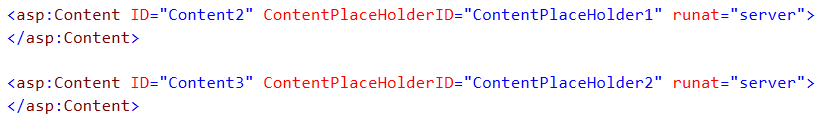
The master page contains a placeholder tag for individual content.

The content page contains a content tag with a reference to the master page.
Advantages on ASP.NET over Traditional ASP
| |
ASP |
ASP.NET |
| Language used |
It uses scripting language. |
It uses programing language like C#, J#, C++. |
| Object oriented approach |
Not object oriented. |
It is object oriented. |
| Debugging |
Debugging is difficult as the ASP scripts are interpreted. |
Errors are generated as compile type errors and therefore debugging is easy. |
| Inheritance |
No concept of inheritance. |
Web forms inherit the code class. |
| Configurable |
Not configurable. |
Web.config is used for configuration. |